Urban Flood Risk Reduction
– A platform to share integrated sustainable practices in Asian Countries
Supported by Asia-Pacific Network for Global Change Research (APN) , Kobe, Japan.
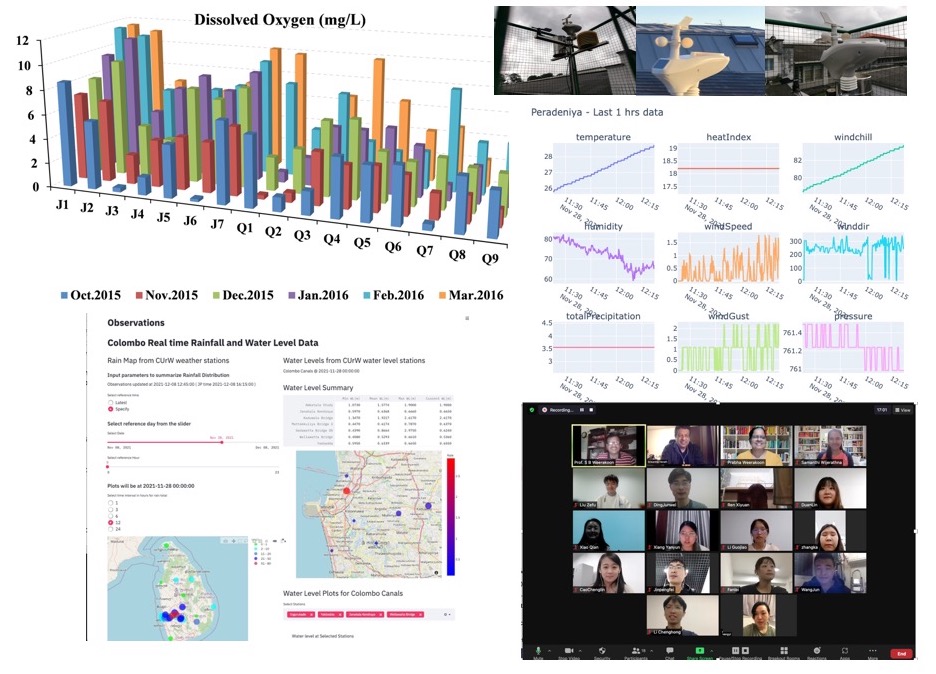
Aim: Develop a platform to monitor and mitigate urban flood risk and improve water quality in coastal Asian countries.
Focus: Assess impacts of climate change and urbanization on water allocation and nutrient levels.
- Climate Change Scenarios: Utilize CMIP6 Socio-economic scenarios centered on SSPs.
- Components of the Platform:
- Flood model: Assess how climate change, river flow, and sea level rise affect surface water levels.
- River nutrient model: Evaluate the impact of climate change, river flow, and land-based human activities on surface water nutrient levels during flood events.
- Coupled model: Serve as a management tool for flood, sediment, and nutrient management in coastal city flood waters.
Integrated Platform: Integrate the three models to create a comprehensive platform for assessing flood, water allocation, and management of water and nutrients in coastal countries.
Addressing Challenges: Tackle excessive runoff (floods), water scarcity (drought), and water pollution caused by climate change and human activities.
Urban-system based adaptation measures: Provide resilience-enhancing measures for the study sites, extendable to traditional urban water management systems, to cope with climate change and urban development.